The cybersecurity community continues to battle an intensifying wave of ransomware attacks in 2025. Far from declining, these attacks have surged to unprecedented levels, targeting organizations across all sectors and geographies. What makes 2025 particularly alarming is not just the volume of attacks, but the sophistication and ruthlessness with which cybercriminals are executing them.
Record-Breaking Attack Numbers
Through October 21, 2025, ransomware groups claimed 5,010 attacks on their dark web data leak sites, representing a 50% increase from the 3,335 attacks during the same period in 2024. This spike represents one of the steepest year-over-year increases in recent memory.
The first quarter of 2025 set an ominous tone. Reported ransomware incidents in the United States increased by 149% year-over-year in the first five weeks of 2025, with 378 attacks compared to 152 during the same period in 2024. These figures demonstrate that attackers are not slowing down despite increased awareness and defensive measures.
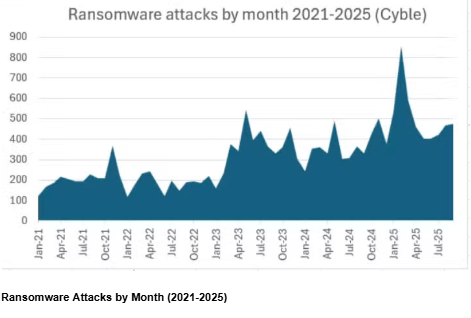
Financial losses continue to escalate alongside attack volumes. Coalition, an active insurance provider, noted that the average ransomware insurance claim rose 68% to $353,000. Organizations paying ransoms reported even more staggering figures, with average payments reaching $2 million, up from $400,000 in 2023.
Critical Infrastructure Under Siege
Manufacturing, healthcare, and financial services have emerged as prime targets for ransomware operators in 2025. Between January and September 2025, 4,701 ransomware incidents were recorded globally, with 2,332 attacks—or 50%—targeting critical infrastructure sectors, marking a 34% year-over-year increase.
The manufacturing sector experienced the most dramatic growth. Attacks against manufacturing surged from 520 incidents to 838, marking a 61% increase. High-profile incidents paralyzed production lines, disrupted global supply chains, and caused millions in losses. From automotive giants to component manufacturers, no segment remained immune.
Healthcare continues to bear the brunt of these attacks despite the life-or-death nature of its operations. Attackers show no hesitation in targeting hospitals, clinics, and medical device manufacturers. The sector’s reliance on interconnected systems and its inability to tolerate downtime make it an attractive target for extortion.
The cybersecurity community continues to battle an intensifying wave of ransomware attacks in 2025. Far from declining, these attacks have surged to unprecedented levels, targeting organizations across all sectors and geographies. What makes 2025 particularly alarming is not just the volume of attacks, but the sophistication and ruthlessness with which cybercriminals are executing them.
Record-Breaking Attack Number
Through October 21, 2025, ransomware groups claimed 5,010 attacks on their dark web data leak sites, representing a 50% increase from the 3,335 attacks during the same period in 2024. This spike represents one of the steepest year-over-year increases in recent memory.
The first quarter of 2025 set an ominous tone. Reported ransomware incidents in the United States increased by 149% year-over-year in the first five weeks of 2025, with 378 attacks compared to 152 during the same period in 2024. These figures demonstrate that attackers are not slowing down despite increased awareness and defensive measures.

Financial losses continue to escalate alongside attack volumes. Coalition, an active insurance provider, noted that the average ransomware insurance claim rose 68% to $353,000. Organizations paying ransoms reported even more staggering figures, with average payments reaching $2 million, up from $400,000 in 2023.
Critical Infrastructure Under Siege
Manufacturing, healthcare, and financial services have emerged as prime targets for ransomware operators in 2025. Between January and September 2025, 4,701 ransomware incidents were recorded globally, with 2,332 attacks—or 50%—targeting critical infrastructure sectors, marking a 34% year-over-year increase.
The manufacturing sector experienced the most dramatic growth. Attacks against manufacturing surged from 520 incidents to 838, marking a 61% increase. High-profile incidents paralyzed production lines, disrupted global supply chains, and caused millions in losses. From automotive giants to component manufacturers, no segment remained immune.
Healthcare continues to bear the brunt of these attacks despite the life-or-death nature of its operations. Attackers show no hesitation in targeting hospitals, clinics, and medical device manufacturers. The sector’s reliance on interconnected systems and its inability to tolerate downtime make it an attractive target for extortion.
Who's Being Targeted?
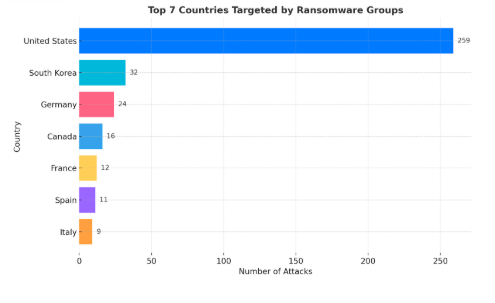
The United States remains by far the biggest target for ransomware groups, with 259 victims accounting for nearly 55% of attacks in September 2025. American organizations face relentless pressure from cybercriminal syndicates who recognize the country’s digital infrastructure and willingness to pay ransoms.
Beyond the U.S., Germany, France, Canada, Spain, Italy and the UK remain consistent targets, but South Korea emerged as a new major target, in second place behind the U.S. with 32 attacks. This geographic diversification reflects the global nature of modern ransomware operations.
The Changing Face of Ransomware Groups
The emergence of The Gentlemen was a noteworthy development, a new group that has claimed 46 victims to date, with their use of custom tools targeting specific security vendors and the geographic diversity of its targets suggesting that the group may have the resources to become an enduring threat.
The ransomware ecosystem underwent significant upheaval in 2025. From the decline of RansomHub to the rise of Qilin and newcomers like Sinobi and The Gentlemen, ransomware group leadership has been in flux for much of 2025, but affiliates have been quick to find new opportunities.
The emergence of The Gentlemen was a noteworthy development, a new group that has claimed 46 victims to date, with their use of custom tools targeting specific security vendors and the geographic diversity of its targets suggesting that the group may have the resources to become an enduring threat.
Attack Vectors and Techniques
The methods attackers use to breach organizations have become more varied and sophisticated. Exploited vulnerabilities have become the primary entry point, accounting for 32% of ransomware incidents in 2025. Organizations struggling to patch known vulnerabilities find themselves particularly exposed.
Compromised credentials accounted for 23% of ransomware attacks in 2025, down from 29% in 2024, while phishing attacks increased to 18%, up from 11% in 2024. The rise in phishing attacks correlates with the increasing use of artificial intelligence to create more convincing lures and social engineering tactics.
Attackers have also accelerated their timelines. The median time from initial intrusion to ransomware execution has decreased, forcing security teams to detect and respond to threats more quickly than ever before.
Who's Being Targeted?
The United States remains by far the biggest target for ransomware groups, with 259 victims accounting for nearly 55% of attacks in September 2025. American organizations face relentless pressure from cybercriminal syndicates who recognize the country’s digital infrastructure and willingness to pay ransoms.
Beyond the U.S., Germany, France, Canada, Spain, Italy and the UK remain consistent targets, but South Korea emerged as a new major target, in second place behind the U.S. with 32 attacks. This geographic diversification reflects the global nature of modern ransomware operations.

The Changing Face of Ransomware Groups
The ransomware ecosystem underwent significant upheaval in 2025. From the decline of RansomHub to the rise of Qilin and newcomers like Sinobi and The Gentlemen, ransomware group leadership has been in flux for much of 2025, but affiliates have been quick to find new opportunities.
Qilin became the most active ransomware group by June 2025, carrying out 81 attacks in a single month, a sharp 47.3% rise. The group’s dominance demonstrates how quickly power shifts in the criminal underground. Meanwhile, Dragonforce surged dramatically, with attacks jumping 212.5%.
The emergence of The Gentlemen was a noteworthy development, a new group that has claimed 46 victims to date, with their use of custom tools targeting specific security vendors and the geographic diversity of its targets suggesting that the group may have the resources to become an enduring threat.
Attack Vectors and Techniques
The methods attackers use to breach organizations have become more varied and sophisticated. Exploited vulnerabilities have become the primary entry point, accounting for 32% of ransomware incidents in 2025. Organizations struggling to patch known vulnerabilities find themselves particularly exposed.
Compromised credentials accounted for 23% of ransomware attacks in 2025, down from 29% in 2024, while phishing attacks increased to 18%, up from 11% in 2024. The rise in phishing attacks correlates with the increasing use of artificial intelligence to create more convincing lures and social engineering tactics.
Attackers have also accelerated their timelines. The median time from initial intrusion to ransomware execution has decreased, forcing security teams to detect and respond to threats more quickly than ever before.
Multi-Extortion: The New Normal
Multi-extortion schemes have become prominent, combining data encryption with data theft to pressure victims. Attackers no longer rely solely on encryption to force payment. They exfiltrate sensitive data before deploying ransomware, threatening to publish stolen information if victims refuse to pay or attempt to restore from backups.
This double-extortion tactic puts organizations in an impossible position. Even with robust backup systems, the threat of data exposure can compel payment. Some groups have adopted triple-extortion methods, targeting customers, partners, or employees of the original victim to increase pressure.
Ransomware-as-a-Service Fuels Growth
Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) continues to fuel the rise in attacks by lowering barriers for hackers. This business model allows technically unsophisticated criminals to launch sophisticated attacks by partnering with established ransomware operators who provide the tools, infrastructure, and support.
RaaS platforms operate like legitimate software businesses, complete with customer support, user forums, and regular updates. This professionalization of cybercrime has democratized ransomware attacks, enabling a broader range of threat actors to participate in the ecosystem.
Emerging Threats: Cloud and AI
Cloud environments are increasingly targeted through misconfigurations and weak access controls. As organizations migrate more infrastructure and data to cloud platforms, attackers have adapted their tactics. Misconfigured S3 buckets, weak identity management, and inadequate network segmentation provide entry points for determined adversaries.
Artificial intelligence has emerged as both a defensive tool and an offensive weapon. Attackers use AI to automate reconnaissance, craft personalized phishing messages, and identify vulnerable targets at scale. This technological arms race shows no signs of slowing.
Multi-Extortion: The New Normal
Multi-extortion schemes have become prominent, combining data encryption with data theft to pressure victims. Attackers no longer rely solely on encryption to force payment. They exfiltrate sensitive data before deploying ransomware, threatening to publish stolen information if victims refuse to pay or attempt to restore from backups.
This double-extortion tactic puts organizations in an impossible position. Even with robust backup systems, the threat of data exposure can compel payment. Some groups have adopted triple-extortion methods, targeting customers, partners, or employees of the original victim to increase pressure.
Ransomware-as-a-Service Fuels Growth
Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) continues to fuel the rise in attacks by lowering barriers for hackers. This business model allows technically unsophisticated criminals to launch sophisticated attacks by partnering with established ransomware operators who provide the tools, infrastructure, and support.
RaaS platforms operate like legitimate software businesses, complete with customer support, user forums, and regular updates. This professionalization of cybercrime has democratized ransomware attacks, enabling a broader range of threat actors to participate in the ecosystem.
Emerging Threats: Cloud and AI
The methods attackers use to breach organizations have become more varied and sophisticated. Exploited vulnerabilities have become the primary entry point, accounting for 32% of ransomware incidents in 2025. Organizations struggling to patch known vulnerabilities find themselves particularly exposed.
Compromised credentials accounted for 23% of ransomware attacks in 2025, down from 29% in 2024, while phishing attacks increased to 18%, up from 11% in 2024. The rise in phishing attacks correlates with the increasing use of artificial intelligence to create more convincing lures and social engineering tactics.
Attackers have also accelerated their timelines. The median time from initial intrusion to ransomware execution has decreased, forcing security teams to detect and respond to threats more quickly than ever before.
Building Resilience Against Ransomware
Organizations must adopt comprehensive security strategies to defend against the ransomware onslaught. DTS Solution specializes in helping businesses implement robust cybersecurity frameworks that address the full spectrum of ransomware threats.
Key defensive measures include:
Vulnerability Management: Threat groups including LockBit, Clop, ALPHV/BlackCat, and RansomHub continue to exploit unpatched vulnerabilities and misconfigured networks. Regular vulnerability assessments and prompt patching remain critical. DTS Solution’s Vulnerability and Patch Management services help organizations identify and remediate weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Network Segmentation: Proper network segmentation limits lateral movement if attackers breach perimeter defenses. Zero Trust and Private Access solutions ensure that compromised credentials or systems cannot provide unfettered access to entire networks.
Endpoint Protection: With ransomware spreading rapidly across connected devices, robust endpoint and server protection creates critical barriers against malware execution and data exfiltration.
Backup and Recovery: Maintaining secure, tested backups remains essential. Organizations must ensure backups are isolated from production networks and regularly validated to guarantee successful restoration when needed.
Security Monitoring: Organizations must prioritize proactive defenses, real-time visibility, and robust incident response plans to remain resilient through 2025 and beyond. Security Intelligence Operations provides the continuous monitoring necessary to detect threats before they escalate.
Incident Response Planning: When attacks occur, having a tested incident response plan dramatically reduces recovery time and minimizes damage. Organizations must prepare for the worst while working to prevent it.
Employee Training: Since phishing remains a primary attack vector, regular security awareness training helps employees recognize and report suspicious activities before they lead to breaches.
Conclusion
The ransomware crisis shows no signs of abating as 2025 progresses. Attackers continue to innovate, finding new vulnerabilities to exploit and new ways to pressure victims into paying. The professionalization of cybercrime through RaaS platforms ensures a steady supply of motivated adversaries.
Organizations can no longer treat ransomware as a hypothetical threat. The question is not whether an organization will face a ransomware attack, but when. Those that invest in comprehensive security strategies, maintain vigilant monitoring, and prepare robust response capabilities stand the best chance of surviving and recovering from these inevitable incidents.
The cost of inaction far exceeds the investment required for proper cybersecurity. As attack volumes surge and financial damages escalate, every organization must assess its vulnerabilities and strengthen its defenses. The criminals behind ransomware attacks are counting on complacency and unpreparedness. Proving them wrong requires commitment, resources, and expert guidance.
For organizations seeking to enhance their ransomware defenses and overall security posture, partnering with experienced cybersecurity providers like DTS Solution can make the difference between becoming another statistic and successfully defending against the growing ransomware threat.
Building Resilience Against Ransomware
Organizations must adopt comprehensive security strategies to defend against the ransomware onslaught. DTS Solution specializes in helping businesses implement robust cybersecurity frameworks that address the full spectrum of ransomware threats.
Key defensive measures include:
Vulnerability Management: Threat groups including LockBit, Clop, ALPHV/BlackCat, and RansomHub continue to exploit unpatched vulnerabilities and misconfigured networks. Regular vulnerability assessments and prompt patching remain critical. DTS Solution’s Vulnerability and Patch Management services help organizations identify and remediate weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Network Segmentation: Proper network segmentation limits lateral movement if attackers breach perimeter defenses. Zero Trust and Private Access solutions ensure that compromised credentials or systems cannot provide unfettered access to entire networks.
Endpoint Protection: With ransomware spreading rapidly across connected devices, robust endpoint and server protection creates critical barriers against malware execution and data exfiltration.
Backup and Recovery: Maintaining secure, tested backups remains essential. Organizations must ensure backups are isolated from production networks and regularly validated to guarantee successful restoration when needed.
Security Monitoring: Organizations must prioritize proactive defenses, real-time visibility, and robust incident response plans to remain resilient through 2025 and beyond. Security Intelligence Operations provides the continuous monitoring necessary to detect threats before they escalate.
Incident Response Planning: When attacks occur, having a tested incident response plan dramatically reduces recovery time and minimizes damage. Organizations must prepare for the worst while working to prevent it.
Employee Training: Since phishing remains a primary attack vector, regular security awareness training helps employees recognize and report suspicious activities before they lead to breaches.
Conclusion
The ransomware crisis shows no signs of abating as 2025 progresses. Attackers continue to innovate, finding new vulnerabilities to exploit and new ways to pressure victims into paying. The professionalization of cybercrime through RaaS platforms ensures a steady supply of motivated adversaries.
Organizations can no longer treat ransomware as a hypothetical threat. The question is not whether an organization will face a ransomware attack, but when. Those that invest in comprehensive security strategies, maintain vigilant monitoring, and prepare robust response capabilities stand the best chance of surviving and recovering from these inevitable incidents.
The cost of inaction far exceeds the investment required for proper cybersecurity. As attack volumes surge and financial damages escalate, every organization must assess its vulnerabilities and strengthen its defenses. The criminals behind ransomware attacks are counting on complacency and unpreparedness. Proving them wrong requires commitment, resources, and expert guidance.
For organizations seeking to enhance their ransomware defenses and overall security posture, partnering with experienced cybersecurity providers like DTS Solution can make the difference between becoming another statistic and successfully defending against the growing ransomware threat.
See also:

