Ransomware Incident Response Plan - Part 1
In a properly implemented crypto viral extortion attack, recovering the files without the decryption key is an intractable problem and difficult to trace digital currencies such as Ukash or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency are used for the ransoms, making tracing and prosecuting the perpetrators difficult. As was already said we will divide the incident response plan into 5 phases and first phase is preparation from we shall start.
Ransomware Incident Response Plan-Part 1
In a properly implemented crypto viral extortion attack, recovering the files without the decryption key is an intractable problem and difficult to trace digital currencies such as Ukash or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency are used for the ransoms, making tracing and prosecuting the perpetrators difficult. As was already said we will divide the incident response plan into 5 phases and first phase is preparation from we shall start.
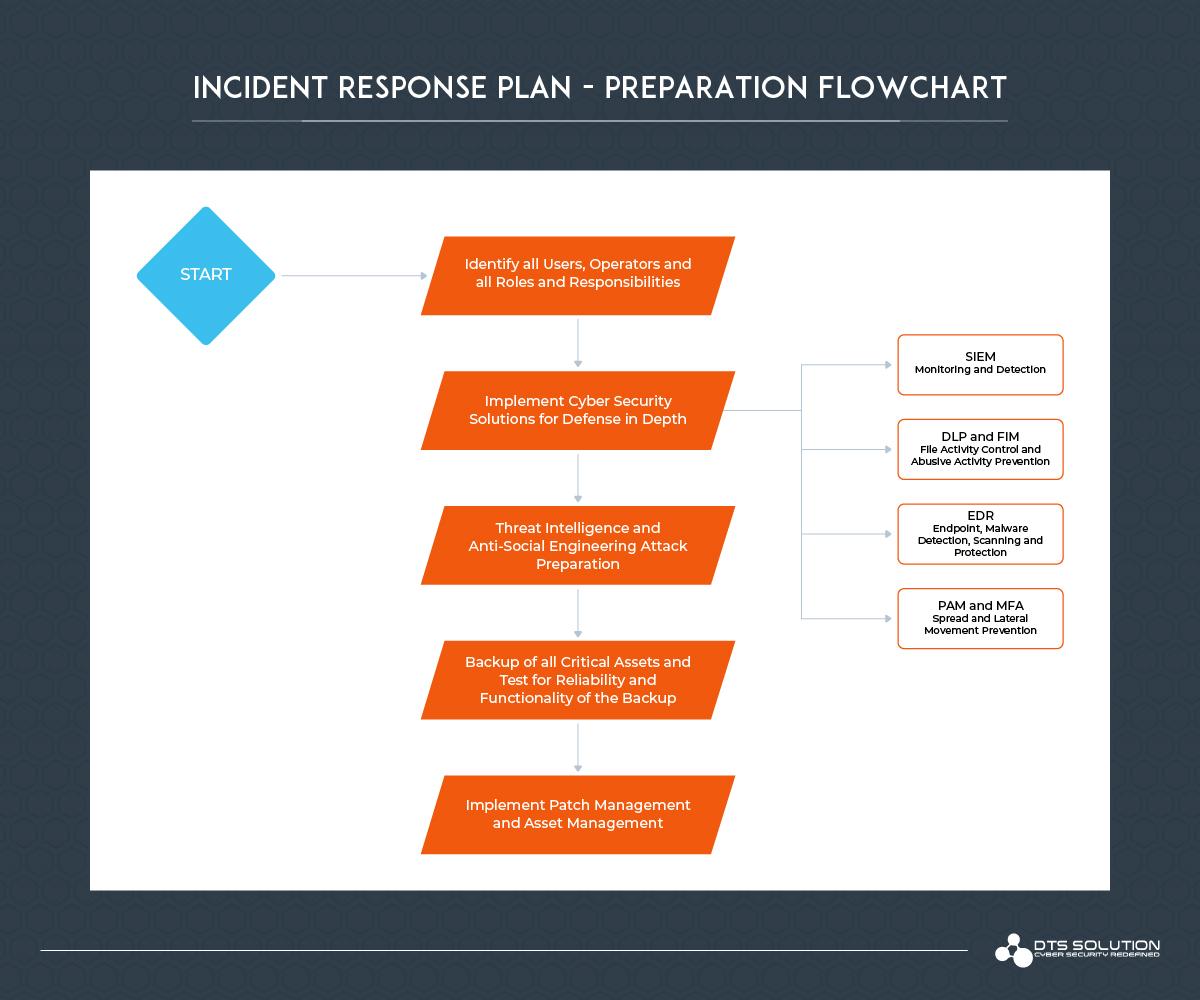
1. Preparation Overview
The recommended practice for backup is to periodically test the backups and verify the validity and reliability of the backups. For being ready and prepared there is yet another crucial step to cover to stay on the safest side and that is to deploy preventive cybersecurity resources. This can range from an anti-malware solution that includes endpoint or heuristic monitoring to advanced EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response) solution. Compared to the traditional anti-virus solutions which only detects malware at a signature level which can be ineffective in case of a new-born ransomware. Hence, we must implement advanced threat detection systems for cyber security resilience. The company or the incident response team should develop an incident response (IR) plan that is created specifically for a ransomware attack. It is crucial to prepare for targeted attacks that can affect broad swaths of your company.
1. Preparation Overview
The recommended practice for backup is to periodically test the backups and verify the validity and reliability of the backups. For being ready and prepared there is yet another crucial step to cover to stay on the safest side and that is to deploy preventive cybersecurity resources. This can range from an anti-malware solution that includes endpoint or heuristic monitoring to advanced EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response) solution. Compared to the traditional anti-virus solutions which only detects malware at a signature level which can be ineffective in case of a new-born ransomware. Hence, we must implement advanced threat detection systems for cyber security resilience. The company or the incident response team should develop an incident response (IR) plan that is created specifically for a ransomware attack. It is crucial to prepare for targeted attacks that can affect broad swaths of your company.
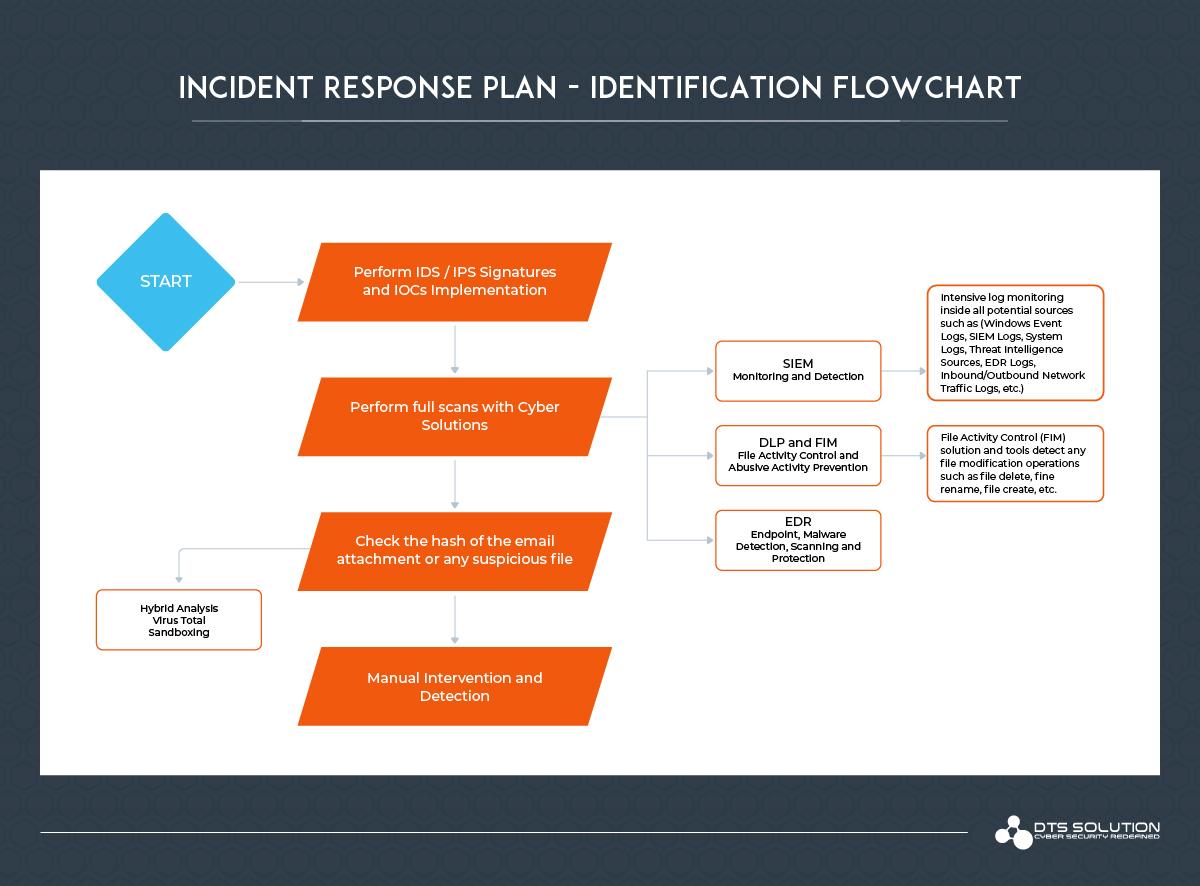
2. Identification
2. Identification
For initial identification and detection, a good approach is to get signatures and IOCs into your IDS. It is highly recommended as a best practice to use a threat intelligence sources to block and alert on the presence of anomalies that have a chance of being associated with ransomware in your network traffic. There are numerous signatures for most of the popular ransomwares out there such WannaCry and NotPetya traffic. These practice alone will not protect you from a ransomware because ransomwares can be modified and changed hence, we want to have more defense than just the detection. However, these signatures can be a useful source for the most widely distributed tools that enterprises tend to use.
See also: